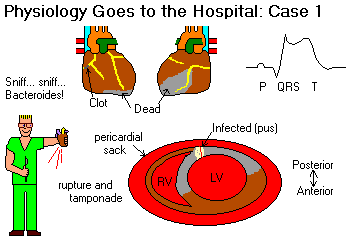

Abe, 62 year old man, brought to the hospital by his wife after complaining of mild ache in the neck, diffuse sweating, and weakness. Diabetic with a lifelong history of deep vein thrombi in the legs. Upon arriving in the emergency room, had an episode of ventricular fibrillation from which he was resuscitated. Thin and tired-looking. Cervical (jugular) venous pressure is low-normal. Loud S3 and S4 gallops. Temp 97.6o, pulse 80, resp 12, BP 105/70. EKG showed normal rhythm with rate 86, PR interval 0.22, QRS duratino 0.12, QT interval 0.40, ST segments markedly elevated in leads 2, 3, and aVF, depressed in leads I, aVL, and V1 through V6. Chest x-ray normal. On the second day, the pulse fell to 60, and BP to 90 systolic or below, and a pacer wire was inserted via the left external jugular vein into a position high in the right atrium, and the heart was successfully paced at a rate of 90. On the seventh hospital day, the pacemaker was withdrawn, an EKG showed normal rhythm of 65 with prominent Q-waves and slightly elevated ST segments in leads 2, 3, and aVF. On the ninth hospiatl day, the patient developed a fever and shaking chills. These continued, without a focus of sepsis being found, until the thirteenth hospital day, when the patient abruptly lost consciousness and quickly died during a chill.
You will see these pictures in class.
What caused the neck pain?
How do you judge jugular venous pressure on physical exam?
Why the drop in blood pressure on admission? Mention several reasons.
Why can death of part of the heart cause the heart to beat more slowly?
Why can lack of oxygen even to a small portion of the heart cause it to beat chaotically and thus ineffectively?
Can you explain the classic EKG findings seen in this case? From the standpoint of a physiologist, of course!
Why doesn't the dead area come right up to the clot?
Why the S3 and S4 gallops?
Why was this man's death so sudden?
If the doctors had been able to examine this man just as his heart ruptured, what would they have seen happen to his neck veins?
In slow tamponade, what are some things that happen when you take a deep breath in?
Main Page
Case 1
Case 2
Case 3
Case 4
Case 5
Ed's Pathology Notes
Ed's Home Page
Bryan's Home Page